
Nexsan NST2000
Entry Level Unified Hybrid Storage Appliance

This product is no longer available, please Contact Us for replacement solution.
Overview:
The Nexsan NST2000 is a modern hybrid storage appliance, a more efficient, agile and intelligent alternative to traditional storage arrays, filers, and all-flash arrays. Organizations have different needs for performance, capacity and connectivity when managing and protecting the data that drives your business. The NST2000 blends solid-state technology, a scalable back-end storage infrastructure, multiple NAS/iSCSI/FC front-end connections, and enterprise-class data management services in a single system. It gives you the convenience and control to meet the needs of one or more workloads in one dedicated easy-to-use appliance.
For organizations struggling to meet both high performance and high capacity NAS, FC or iSCSI application requirements, the NST2000 makes that easy with a hybrid of solid-state accelerated hard drives. For applications with the most stringent workload requirements like server virtualization, desktop virtualization (VDI), databases and cloud computing, the NST2000 delivers unparalleled performance to ensure application demands never outpace available I/O again. Your applications will have never performed faster on a system operating at the economics of spinning disk storage.
Key Benefits
- Smart Hybrid – FASTier flexible hybrid caching provides high performance where it’s needed. NestOS software intelligently optimizes the hybrid storage architecture and resources.
- Agile Scalabilty – Linear, non-disruptive scaling up to 168 Terabytes.
- Efficient Unified – Unified storage system that supports FC, NFS, iSCSI, CIFS, SMB, and FTP in a single software stack and within a single-pane-of-glass management.
- Enterprise Class – Enterprise class Integrated System Data Management, Business Continuity, and Data Protection features and services that are rightsized for the mid-market.
- Hybrid Scaling – With NST, you can scale both FASTier intelligent caching and Hard Disk Drive storage.
- Performance Agility – NST’s FASTier Intelligent caching allows you to tune performance where you need it, apply FASTier to specific applications that require high performance.
- Application Flexibility – Unified storage system that supports multiple application needs through iSCSI, FC, NFS, SMB, and FTP in a single system, with a ‘single pane of glass’ management.
- High-Capacity Scaling – Linear, non-disruptive scaling up to 168TB and storage features such as compression.
Introducing FASTier Caching
The proprietary FASTier caching acceleration technology uses solid-state memory, including SSD, to optimize block and file operations in a fault tolerant architecture. FASTier can scale from 600GB to 2TB. Intelligent, automatic caching algorithms remove the need for manual intervention or applicationspecific tuning. Whereas traditional disk storage is hard pressed to meet high I/O requirements and SSD-only arrays have a very high cost with limited capacity, Imation’s NST2000 Hybrid Storage Appliance realigns the trade-off between performance, capacity and cost so IT administrators can do more than ever before.
Fully Featured
The NST2000 is fully featured with snapshots, replication, thin provisioning, replication, compression, and much more. A revolutionary GUI and scriptable CLI streamline setup and management for the time-constrained IT administrator. As with all storage, the Nexsan NST2000 no single point-of-failure architecture ensures the ultimate in reliability. The net of all this performance and functionality is a true enterprise-class solution without the enterprise-class price.
NST2000 Hybrid Storage Appliance
NST2000 storage systems utilize SSD, NL-SAS or SAS drives; two redundant, high performance, multi-core Xeon-based storage controllers; high speed I/O subsystems and a fully redundant architecture. All active components are hot-swappable, including power supplies, disks and controllers. FASTier read and write cache complements 96GB DRAM to significantly accelerate IOPS and throughput. The NST2000 features 16 Xeon CPU cores, up to 168TB of capacity and up to 2TB of SSD in FASTier cache.
The NST2000 provides CIFS and NFS shared folders as well as fibre channel or iSCSI volumes. Snapshots do not require the pre-reservation of storage capacity, and they may be scheduled and managed easily from the management GUI or initiated from Windows VSS requestors.
Individual shares, LUNs, or entire storage pools may be replicated asynchronously to a second NST2000 storage system, with snapshots intact for use on the target side for backups, testing or data mining. Active Directory integration make it easy to manage user identities and access rights on the NST2000 shares, while CHAP, iSNS and LUN masking protect iSCSI traffic. Quotas limit storage consumption by share, and oversubscription is permitted for thin provisioning storage, along with alarms which notify when additional storage is needed. Capacity can be expanded by adding additional storage to a running system, so future needs can be met without incurring downtime. Moreover, link aggregation combines Ethernet ports for faster throughput.
- FC/iSCSI block and NFS/CIFS shared folders
- FASTier caching acceleration technology
- Snapshots
- Asynchronous replication
- Quotas and thin provisioning
- Online capacity expansion
- Enterprise-class reliability and fault tolerance
- Hot-swappable active components
- Utilize SSD, NL-SAS and SAS drives
- Active Directory, iSNS and CHAP integration
Features:
Enterprise-Class Feature Set
- NAS (CIFS and NFS) Services – Shared Folders can be accessed through CIFS, NFS or both. FTP services are also provided.
- FC & iSCSI Block Services – FC or iSCSI volumes can be provided to physical or virtual servers for direct-attached or SAN connections.
- FASTier Caching – Flash SSD technology is used to accelerate read and write IOPS and throughput. FASTier caching works transparently so there is no administration burden to turbo-charge I/O performance. FASTier caching is especially useful for random I/O workloads such as databases or for VMware, Xen or Hyper-V environments.
- Online Capacity Expansion – Add additional hard drives to any storage pool to increase its capacity on the fly without impacting active clients. I/O will automatically be balanced across all drives.
- Snapshots – There is no performance penalty for taking snapshots. Up to 2048 snapshots are supported. Storage does not need to be reserved to hold snapshot data. The management GUI makes it easy to setup and manage snapshot creation and deletion schedules. Snapshots are mountable for testing or other purposes. Granularity is per pool, per share, or LUN.
- Asynchronous Replication – Asynchronous replication is WAN efficient because it only transmits delta blocks to the destination side. All snapshots taken on the source side are available on the destination side for backups, data mining or testing purposes. Granularity of replication is a storage pool, a share, or a LUN.
- Quotas / Thin Provisioning – More storage can be allocated than actually exists in the system – referred to as oversubscription. Alarms warn of limits reached, so storage can be added.
- Data Compression – Granular inline data compression meaning any file or block that is stored in the NST storage pool can be compressed, yet from the application’s point of view, the file appears to be stored uncompressed.
- Link Aggregation – IEEE 802.3ad link aggregation allows multiple Ethernet ports to be combined for faster throughput.
- Data Protection Suite – Provides NST with snapshot and replication capabilities.
Enterprise-Class Performance and Reliability
- Drive Types – The NST2000 utilizes SSD, SAS 10K RPM or 7.2K RPM drives to meet varying storage needs.
- Dual Storage Controllers – Dual controllers provide a no single point-of-failure solution. Should one controller fail, the second will perform all of the I/O operations as well as utilize its I/O ports for connection to external storage.
- RAID – RAID 5/6/10 are provided to protect against a single drive failure or up to two drives failing at the same time.
- High Availability – All active components are redundant and hot-swappable including power supplies, disks and controllers.
- Controller I/O Ports – Each storage controller provides up to (8) 1Gb Ethernet ports, (4) 10Gb Ethernet ports, and (2) 8Gb/s fibre channel ports
Easy to Manage
- Quick Start wizard – Get the storage system up and running in 15 minutes or less.
- Easy to Manage – A revolutionary GUI design makes it easy to set-up, manage and monitor the storage system. Wizards guide the IT generalist through setup, share and LUN creation and management, snapshots, volume management, replication, clustering, user management and security and setting up alerts.
- Web-based Management – A Web server residing in the storage system presents the management GUI in a Web browser. An extensive CLI permits scripted administration as an alternative to using the GUI. Administer storage systems remotely. There is no need to install management software on a client computer and keep it updated. Use Windows Computer Manager to manage Share/Folder/File permissions for users and groups as well as LUNs.
- Automatic RAID Set Maintenance – In the event of a drive failure, spare drives are automatically added to a RAID set and a RAID set rebuild is run – all without any manual intervention being required.
- Alerts – Alerts are sent via SNMP or email and are stored in system log files. They are transmitted to the Web browser-based management console.
- NTP client – Network Time Protocol client relieves the administrator from having to set, adjust and synchronize clocks across systems.
- NDMP V4 – Backup with popular backup and restore solutions through the industry-standard NDMP V4 interface or backup LUNs using any popular backup and restore applications. NDMP V4 preserves all access rights for CIFS and NFS shares, and uses background snapshots for fast backups.
- Role-based Administration – Storage system administrator can grant limited rights administrators per storage pools. These administrators can create, manage and delete shares and LUNs, perform snapshots and replication, and manage share-level access permissions.
Specifications:
| Hybrid Storage Model | NST 2000 | NST 4000 | NST 6000 |
|---|---|---|---|
| Entry Level | Mid-Range | High-End | |
| Protocols | FC, iSCSI, NFS, CIFS/SMB, FTP | ||
| System Configuration | |||
| Controllers per system | 2 | 2 | 2 |
| System CPU Cores | 16 | 16 | 24 |
| System Memory (DRAM) | 96 GB | 96 GB | 192 - 384 GB |
| FASTier Cache | |||
| Maximum FASTier Capacity | 2TB | 6.4TB | 9.4TB |
| Maximum Number FASTier SSD's | 4 (with storage expansion) | 22 | 46 |
| Read FASTier SSD's | 400 / 800 GB | 400 GB | 200 / 400 / 800 GB |
| Write FASTier Cache | 200/400 GB SSD's | fault tolerate DRAM | fault tolerate DRAM |
| Storage Arrays | |||
| Maximum Raw Capacity | 168TB | 2.1PB | 5PB |
| Storage Chassis | Internal Storage & Expansion | E-Series E60VT, E48VT, E32V, E18VT |
E-Series E60VT, E48VT, E32V, E18VT 224X |
| Maximum Storage Expansion | 1 | 6 | 21 (with SAS switch} |
| Storage Media | |||
| 7.2K RPM SAS HDD's | 2 / 4 / 6 TB | 2 / 4 / 6 / 8 TB | 1 / 2 / 3 / 4 / 6 / 8 TB |
| 10K RPM SAS HDD’s | 600 / 900 / 1,200 GB | 600 / 900 / 1,200 GB | 450 / 600 / 900 / 1,200 / 1,800 GB |
| SSD's | 200 / 400 / 800 GB | 100 / 200 / 400 GB | 100 / 200 / 400 / 800 GB |
| Maximum Number of HDD’s | 44 | 360 | 1,260 |
| Power, Cooling & Environmental | |||
| Number of hot-swappable power supplies | 2 | 2 | 2 |
| Wattage per Controller | 920 W | 420 W | < 430 W |
| Voltage and Frequency | 100-240V, 50-60z | 100-240V, 50-60z | (110) 90-130V, 47-63 Hz (220) 180-246V, 47-63 Hz |
| Operating Temperature | 10-35C (50-95F) | 10-35C (50-95F) | 10-35C (50-95F) |
| Operating Humidity | 20-95% Non Condensing | 20-95% Non Condensing | 20-95% Non Condensing |
| Size & Weight | |||
| System Form Factor | 2U or 3U | 4U | 6U |
| Dimension (W x H x D) | 2U: 17.2 x 3.5 x 26.75 in. (43.7 x 8.9 x 67.9 cm) 3U: 17.2 x 5.2 x 24.2 in. (43.7 x 13.2 x 61.5 cm) |
17.2 x 3.5 x 26.75 in. (43.7 x 8.9 x 67.9 cm) |
17.2 x 3.5 x 27.87 in. (43.7 x 8.9 x 70.79 cm) per controller |
| Controller unit weight (min/max) | 85 lbs. (38.6 kg.) / 90 lbs. (40.8 kg.) | 85 lbs. (38.6 kg.) / 90 lbs. (40.8 kg.) | >40 lbs (18.1Kg) |
 FASTier Acceleration Technology:
FASTier Acceleration Technology:
Nexsan’s FASTier acceleration technology leverages the power of solid-state to accelerate the performance of the underlying spinning disks by a factor of up to 10X. The net result is a radical new cost-per-I/O, allowing organizations to do more than ever before in virtual and cloud environments.
The onset of virtualized environments and cloud-based computing has caused traditional disk-based storage to struggle in keeping pace with the new I/O pressures being placed on it. As the number of virtual machines grow, even the fastest traditional storage with the most powerful controllers are simply not fast enough to scale with the seemingly endless performance demands of a sprawling environment of virtual servers and desktops, mission-critical databases and email servers. The result has been a storage performance bottleneck that keeps companies from fully leveraging the true application power and cost-effectiveness of their virtual and cloud infrastructures.
Enter Solid-state
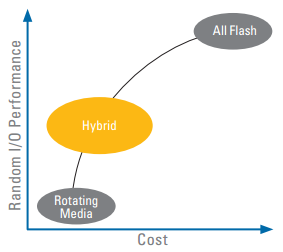
Solid-state performance alleviates storage performance choke-points... but at a price and capacity that is unreasonable for the average organization. In the rush to exploit an emerging marketing opportunity made possible by SSDs, some vendors are providing SSD-only arrays. However, the exorbitant cost and capacity constraints of an SSD-only array have relegated its use to extreme situations. Some vendors have introduced SSDs into their systems with automated tiering software in which data can be migrated from SSD to SAS and/or SATA drives. However, this operation can significantly reduce the performance of the system as data is moved from one tier to another. Auto-tiering presents additional problems as organizations must purchase an inordinate amount of SSD to store their most frequently accessed data because they are housing data rather than caching data. Once data is moved out of the SSDs, it is subject to the slower speed of the spinning disks.
Enter Hybrid Storage
Nexsan’s FASTier acceleration technology has innovatively combined the performance of solid-state with the capacity and cost effectiveness of traditional disk storage. Imagine a Hybrid Storage system as an orchestra. If rotating media is the percussion section and solid-state is the brass section, FASTier is the conductor that makes them work together in harmony to provide the music - a Hybrid Storage system that delivers the speed of solid-state along with the capacity and cost benefits of spinning disk. FASTier’s advanced software architecture and algorithms manage the data that is being read and written, leveraging a modest amount of solid-state to greatly accelerate the performance of the underlying spinning disks by a factor of up to 10X or more.
In this scenario, solid-state is judiciously used to enhance traditional disk-based storage via FASTier to provide new levels of performance where cost and capacity are primary concerns. As a result, a Hybrid Storage system (like Nexsan NST4000) easily eliminates the performance bottlenecks in the most demanding virtual and cloud environments.
This technical brief will survey the landscape of flash-based caching approaches, identifying their strengths and weaknesses, and explore Nexsan FASTier in the Nexsan NST Hybrid Storage system.
Cache Size
Caching techniques are not new to storage systems or application servers. Reads and writes are typically held in high-speed DRAM providing needed acceleration for the underlying hard drives. Frequently requested blocks can be read from the spinning disks and held for a period of time. Smaller writes are also held in DRAM where they are aggregated into larger writes and RAID checksum calculations can be performed before they are pushed to the spinning disks.
FASTier acceleration technology in the NST storage system utilizes up to 192GB of DRAM and up to 2.8TB of 100GB or 200GB flash-based SLC SSDs. The NST is a Hybrid Storage system that contains up to a petabyte of spinning disk storage. FASTier is ideal with that kind of capacity as it accelerates overall storage performance by up to 10X. If the working sets of the application servers fit entirely into the SSD cache, performance can climb even more dramatically.
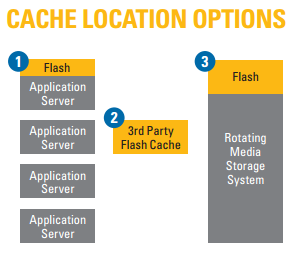 Cache Location
Cache Location
Application Server, Storage System, or In-between
There are three places to introduce cache to accelerate storage performance: (i) in the application server, (ii) in the storage system, and (iii) in an appliance introduced between the application servers and the storage system. Each has its advantages and challenges.
When cache is introduced in the application server itself, it lives on the high speed PCIe bus for maximum bandwidth. Still, since it is a cache, the speeds at which it can be filled and drained must be balanced, lest it remains unfilled, or becomes completely filled. So, bandwidth to the storage system has to be considered. Multiple 8Gb Fibre Channel, 10Gb iSCSI, 24Gb SASx4, or 40Gb Infiniband interconnects may still be needed.
There are four disadvantages to application server-based caching:
- Cache is typically not resilient to a single point-of-failure. It can only be used to cache reads. Writes must be pushed all the way to the storage system before they can be acknowledged safely to the application. The inability to cache writes has a pronounced negative impact on VDI performance and other applications.
- Custom proprietary device drivers need to be installed onto the application servers, a practice that is generally unacceptable or highly questionable to IT administrators.
- Application server-based caches are, by design, a dedicated resource to a single server and thereby reduce operational flexibility and the ROI on the purchase.
- Perhaps most importantly, server CPU cycles are used to run caching algorithms, detracting from the total power available to run applications.
 When storage systems cannot be outfitted with a sufficiently sized cache, a third system can be introduced in between the application servers and the storage system. This is the least beneficial architecture of all, and usually the most expensive.
When storage systems cannot be outfitted with a sufficiently sized cache, a third system can be introduced in between the application servers and the storage system. This is the least beneficial architecture of all, and usually the most expensive.
There are four disadvantages to interstitial appliance-based caching:
- Management is difficult since the appliance cache must be managed separately from the application servers and the spinning disk storage system.
- Should it fail, all the writes that it was caching may be lost. As a write-through cache, only reads are cached, so writes must go all the way through to the spinning disk storage system before they are acknowledged. The result is a significant overall performance loss.
- Support contracts are complicated as storage vendors may simply blame the interstitial appliance in any troubleshooting scenario.
- Many IT administrators avoid interstitial appliance-based caching because the risks are too high and reliability is questionable. The best place for cache to get the greatest storage performance advantage is in the storage system itself.
There are five advantages to storage system caching with FASTier:
- FASTier storage-based caching offers a fault-tolerant architecture, enabling both reads and writes to be cached, which is especially important for supporting virtual desktops.
- No proprietary or unproven device drivers need to be installed on the application servers.
- Since the cache accelerates overall NAS/SAN performance, all application servers that use the storage system will benefit from it.
- The caching algorithms utilize the CPU power and DRAM in the storage system, so application servers are not bogged down.
- Management of the storage system-based cache is usually integrated with overall storage system administration and with other important storage system features such as thin provisioning, online capacity expansion, snapshots and replication.
Flash-only Storage Systems
Rather than use flash-based devices as a cache for spinning disks, some storage systems are flash-only. While the performance numbers are high for such systems because the entire working set fits into flash, the costs are exorbitant while the capacities are extremely low, typically under 50TBs as compared to Hybrid Storage systems that leverage spinning disks to hold up to 1PB or more. What’s more, flash-based SSDs have a much shorter lifespan compared to spinning disks. And when they are configured into a RAID set, the SSDs may experience two writes for every application write – one to store the data, and one to store the RAID5 or RAID6 checksum, further decreasing the lifespan of the SSDs.
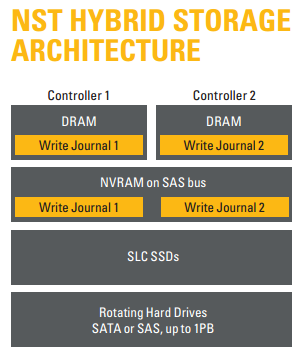 Cache Hardware Architecture
Cache Hardware Architecture
Not all hardware architectures are alike for flash-based caches. Some are not resilient against a single point-of-failure. Therefore, they can only be used as a write-through cache where reads can be cached but writes experience long delays as they are committed to the spinning disks before being acknowledged. FASTier is fully fault-tolerant. It can cache both reads and writes for maximum application performance acceleration.
FASTier Overview
FASTier uses DRAM, NVRAM and flash caching to greatly accelerate reads and writes in concert with the underlying spinning disks. DRAM and NVRAM are important parts of the hardware architecture because they are 20X or more the speed of flash and they do not wear out. FASTier uses flash for both read and write caching. In write caching, the transactions are protected in the DRAM/NVRAMbased write journals until they make it all the way to the spinning disk RAID set, so the flash devices do not need to be in a RAID set. Further, the read cache flash does not need to be configured into RAID sets. Should a read cache flash device fail, it is mapped out and the read is re-issued to the underlying spinning disk. NST Hybrid Storage minimizes the wear on flash-based devices by clever use of DRAM, NVRAM to prolong the overall life of the system.
Cache Software Architecture
The key to FASTier is the software architecture and algorithms that intelligently and automatically use solid-state devices to accelerate the performance of the underlying drives. The FASTier write journal uses the same technique that has been used in large enterprise-class databases such as Oracle, DB2, or Microsoft SQL Server, where writes to the database come in as transactions, are placed into the write journal immediately, then acknowledged to the writer. Later, they are picked up from the write journal and applied to the underlying hard drives. This same technique is used in journaled files systems such as Microsoft’s NTFS and Apple’s HFS Plus journaled file system. Another FASTier algorithm uses DRAM to aggregate smaller writes before sending them to the underlying spinning disks, which increases the ability of the spinning disks to absorb the data efficiently. Opportunistic read-aheads of blocks for applications exhibiting proximate read access patterns also increase system performance. And holding transactions in the write journal until they make it all the way to the underlying drives increases cache performance and minimizes flash wear.
Cache Management Matters
FASTier management is performed within the GUI of the NST storage system. The only decisions are the size of the FASTier read and write caches, the number of FASTier caches per system, and the storage pools that each FASTier cache will be associated with. This level of simplicity is in stark contrast to the complexity of caching features on competing storage systems, server-based caches, or third-party appliance-based caches that live between the application servers and the storage system.
Overall Storage System Considerations
Nexsan’s FASTier acceleration technology utilizes solid-state devices and spinning disks to create a Hybrid Storage system which breaks through the barriers of traditional spinning disk storage. The resulting performance, cost and capacity benefits are far beyond alternative caching architectures and flash-only storage systems. FASTier changes everything. A FASTier enhanced Hybrid Storage system, such as the NST with 7200RPM SATA or NL-SAS drives, can deliver the performance of a system with 15K SAS drives, at one third the cost and in one third the footprint, while using one third the power and cooling. And because FASTier on the NST can be configured up to 2.8TB, it can hold entire working sets to deliver up to 10X the performance of spinning disks and beyond. Alternatively, an NST Hybrid Storage system outfitted with SAS drives and FASTier delivers industry-leading performance and price-per-IOP to power the most demanding virtual computing environments and databases.
Views:

Front View

Front Cover Open View

Rear View
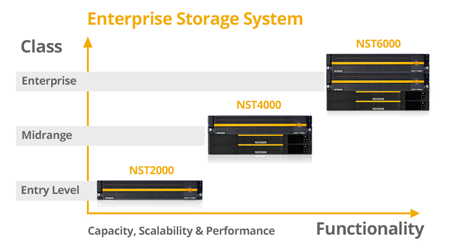 Compare:
Compare:
Surprisingly Powerful Scalable Storage
Nexsan NST delivers a full enterprise-class feature set for small, midsize, and large businesses. NST’s FASTier hybrid caching accelerates performance to meet demanding I/O requirements. This unified platform supports Fibre Channel and iSCSI connectivity in addition to NAS and SAN protocols. Hybrid HDD and SDD support can be tailored for the best mixed application deployment environment. For organizations facing extreme data growth or needing greater application performance, Nexsan NST scales from 13TB up to 5PB.
 |
 |
 |
|
| NST2000 | NST4000 | NST6000 | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Max. System Storage Capacity | 168TB | 2.1PB | 5PB |
| Rackmount Form Factor | 2U (4U with Expansion) | 3U (6U with Expansion) | 6U (42U with Expansion) |
| Network Connectivity | GigE, 10GigE, 8Gb FC | GigE, 10GigE, 8Gb FC | GigE, 10GigE, 8Gb FC |
| NAS: CIFS/SMB & FTP Protocols | |||
| SAN: FC & iSCSI Protocols | |||
| Ideal for: Larger Data Sets | |||
| Mixed Workloads | |||
| Critical Applications |
Documentation:
Download the Nexsan NST Family Hybrid Storage Data Sheet (PDF)
Download the Nexsan NST2000 Data Sheet (PDF)
Download the Nexsan NST2000 Spec Sheet (PDF)

